By Kate Torgovnick May
You don’t “find your calling,” you fight for it — and other lessons from people who found their passion (sometimes late in life).
Whether it was during a career aptitude test or in a heart-to-heart chat, chances are someone has talked to you about how to “find your calling.” It’s one of those phrases people toss about. But StoryCorpsfounder Dave Isay takes issue with it … specifically, the verb. “Finding your calling — it’s not passive,” he says. “When people have found their calling, they’ve made tough decisions and sacrifices in order to do the work they were meant to do.” In other words, you don’t just “find” your calling — you have to fight for it. And it’s worth the fight. “People who’ve found their calling have a fire about them,” says Isay, the winner of the 2015 TED Prize. “They’re the people who are dying to get up in the morning and go do their work.” Over a decade of listening to StoryCorps interviews, Isay noticed that people often share the story of how they discovered their calling — and now, he’s collected dozens of great stories on the subject into a new book, Callings: The Purpose and Passion of Work. Below, he shares 7 takeaways from the hard-won fight to find the work you love.
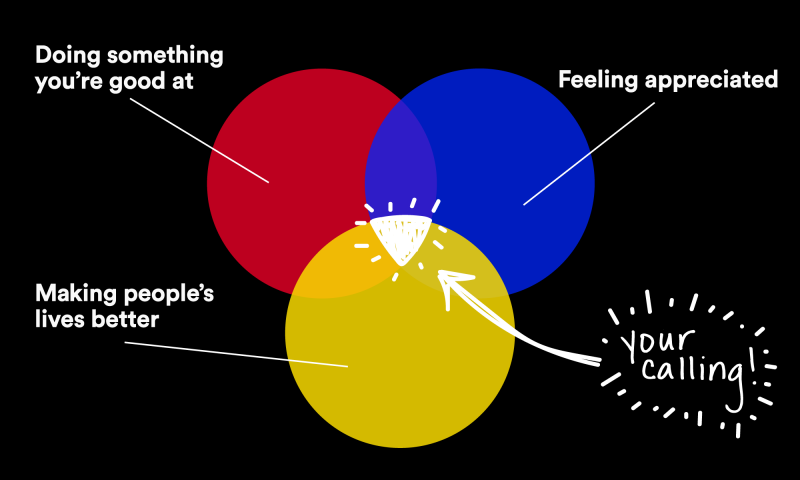
1. Your calling is at the intersection of a Venn diagram of three things: doing something you’re good at, feeling appreciated, and believing your work is making people’s lives better. “When those three things line up, it’s like lightning,” Isay says. He doesn’t suggest that a person has to be a surgeon saving lives to feel like they have a calling; think of the diner waitress who talks to customers and makes them feel loved. How do you find this overlap? “You have to shut out all the chatter of what your friends are telling you to do, what your parents are telling you to do, what society is telling you to do,” Isay says, “and just go to that quiet place inside you that knows the truth.”
2. Your calling often comes out of difficult experiences. What lurks in that quiet place will be a defining experience — quite possibly a painful one. Isay points to an interview in Callings with 24-year-old teacher Ayodeji Ogunniyi. “He was studying to be a doctor when his father was murdered. He realized that what he was really meant to do was be a teacher,” says Isay. “He says that every time he walks into a classroom, his father is walking in with him.” This theme of people turning their hardest experiences into a new path runs throughout the book. “Having an experience that really shakes you and reminds you of your mortality can be a very clarifying event in people’s lives. Oftentimes, it leads to changes,” he says. “We spend a lot of time working, so it can really change your priorities in terms of work life.”
3. Calling often takes courage and ruffles feathers. Elsewhere in Callings, we hear about Wendell Scott, who became the first African-American NASCAR driver in 1952, and kept on driving despite threats against his life. From scientist Dorothy Warburton who dealt with extreme sexism as she conducted research to break the stigma around miscarriage. From Burnell Cotlon, who opened the first grocery store in the Lower 9th Ward after Hurricane Katrina because he wasn’t about to let his old neighborhood’s spirit fade. Calling, says Isay, very often starts with taking a stand against a status quo that simply isn’t acceptable, and then dedicating your work to changing it: “It’s work ignited by hope, love, or defiance — and stoked by purpose and persistence.”
4. Other people often nudge you toward your calling. Sharon Long had worked odd jobs most of her life. As Isay tells it, “Her daughter was going to college, and as the bursar was helping them with financial aid forms, she said quietly to herself, ‘I wish I could’ve gone to college.’ The bursar responded, ‘It’s not too late.’” Sharon enrolled in an art program, and on her advisor’s suggestion, took forensic anthropology as her science. “The advisor suggested it for no other reason than he thought it was the easiest science course for the science requirement,” says Isay. “But the minute she sat in that class, it was boom — this is what she was meant to do.” Isay tells this story to illustrate how calling, while very personal, is also relational. “People bump you this way and that way,” he says, often without realizing it. “When people find their callings, they want to honor those people who helped them get there.”
5. What comes after identifying your calling is what really matters. The old ‘finding your calling’ phraseology makes it sound like a calling is a pot of gold at the end of the rainbow — you find it, and the story’s over. But Isay stresses that your calling is an ongoing process. “Understanding what your calling is — that’s very different than the blood, sweat and tears of actually doing it,” he says. Pursuing a calling may require going back to school or apprenticing; it may require starting a business. Often, notes Isay, it leads a person into a line of work that’s in service of others. “This book is basically a love letter to nurses, teachers, social workers — the people who don’t often get celebrated for the work they do,” he says.
6. Age is irrelevant. Isay found his calling when he was 21 and interviewed a man who’d been part of the Stonewall riots. “The minute I hit record, I knew that being a journalist and interviewing people was what I was going to do for the rest of my life,” he says. “I feel very lucky that lightning struck when I was very young.” But collecting stories for the book reminded him that a calling can be discovered at any age. The book includes an interview with someone who knew they wanted to be an NBA referee at age 15, and another who worked as an accountant for 30 years before discovering his passion for slicing lox. “Doing the work you’re meant to do is one of the most satisfying, remarkable experiences that a person can have,” says Isay, “so never give up.”
7. Calling often doesn’t come with a big paycheck. Another trend Isay sees in stories of people who find their calling: they often involve leaving a high-paying job for one that’s lower-paying but more satisfying. “The message we send to young people is that you want to do as little work as you can to make as much money as you can — that’s the dream,” says Isay. “But the wisdom in the StoryCorps archive is that there’s another, much more rewarding dream of taking risks and working very hard to live with integrity.” In the end, that’s the lesson he took away from writing this book. “There are no millionaires, no billionaires, no celebrities, nobody with a big Twitter following,” he says. “Just stories that can teach us a lot about lives fully lived.”
This article first appeared on Ideas.ted.com. To learn more about StoryCorps and the TED Prize, watch this TED-Ed Original video.
Featured image: Emily Pidgeon/TED